 The Nampa Image, unearthed 312 ft deep while drilling
The Nampa Image, unearthed 312 ft deep while drilling
Human artifacts and remains related to the Flood
All over the world, human remains and artifacts have been located in the process of mining, quarrying, road building, excavation or exposed by natural erosion.
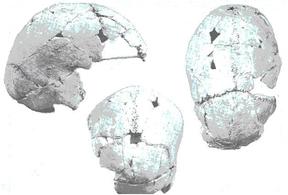
Nampa Image (Left)
Wright, Frederick, G. American Antiquarian 11:379-381 1889 and Scientific American, Nov. 9, 1889.
An Image from Nampa, Idaho area was brought to the surface in a well drilling operation in 1889. The stone doll came from the 300-foot level of a well boring. “The record of the well shows that in reaching the stratum from which the image was brought up they had penetrated first about fifty feet of soil, then about fifteen feet of basalt, and afterwards passed through alternate beds of clay and quicksand down to a depth of about three hundred feet, when the sand pump began to bring up numerous clay balls, some of them more than two inches in diameter, densely coated with iron oxide." According to the United States Geological Survey the age of this strata "Plio-Pleistocene” was 2 million years ago using non-catastrophic measurements. It should be noted that the well log shows the image was found a bed of sand and far below a 15 foot lava layer of the Columbia basalts. These cover over 80,000 square miles of the Northwestern United States to a thickness measured in miles, which suggest they were laid down during the flood period. In this find we have evidence that a civilization existed before the catastrophe that covered the idol, confounding current Geological and Archeological origin's models but fully support a Biblical one.
For over 150 years artifacts and the remains of fully modern human beings have been discovered in rocks of the earth. When such items are found and presented to authorities, these "authorities" (the general public thinks scientific and objective), the artifacts and/or remains are immediately rejected out of hand, deemed invalid due to their wrong placement in the preconceived picture of evolution based archaeology, geology and other related sciences. As these adhere to the same evolution model, a model that assumes man evolved from apes some hundreds of thousands of years ago and much further, so any evidence found to the contrary is ignored and tossed aside. A common example we will soon document is that articles and even human remains that are found in coal. As coal is considered quite old in the evolutionary scale of things, (often more than 200 million years), any such finding should controvert the entire premise of human evolution by huge epochs of time. Here I have included in a plethora of evidence in support the Flood account. As such, if the Flood (in strict adherence to the Biblical account) occurred, we should be able to enter the fields of Archaeology, Paleontology and Geology and find this obvious evidence.
All over the world, human remains and artifacts have been located in the process of mining, quarrying, road building, excavation or exposed by natural erosion.
Nampa Image (Left)
Wright, Frederick, G. American Antiquarian 11:379-381 1889 and Scientific American, Nov. 9, 1889.
An Image from Nampa, Idaho area was brought to the surface in a well drilling operation in 1889. The stone doll came from the 300-foot level of a well boring. “The record of the well shows that in reaching the stratum from which the image was brought up they had penetrated first about fifty feet of soil, then about fifteen feet of basalt, and afterwards passed through alternate beds of clay and quicksand down to a depth of about three hundred feet, when the sand pump began to bring up numerous clay balls, some of them more than two inches in diameter, densely coated with iron oxide." According to the United States Geological Survey the age of this strata "Plio-Pleistocene” was 2 million years ago using non-catastrophic measurements. It should be noted that the well log shows the image was found a bed of sand and far below a 15 foot lava layer of the Columbia basalts. These cover over 80,000 square miles of the Northwestern United States to a thickness measured in miles, which suggest they were laid down during the flood period. In this find we have evidence that a civilization existed before the catastrophe that covered the idol, confounding current Geological and Archeological origin's models but fully support a Biblical one.
For over 150 years artifacts and the remains of fully modern human beings have been discovered in rocks of the earth. When such items are found and presented to authorities, these "authorities" (the general public thinks scientific and objective), the artifacts and/or remains are immediately rejected out of hand, deemed invalid due to their wrong placement in the preconceived picture of evolution based archaeology, geology and other related sciences. As these adhere to the same evolution model, a model that assumes man evolved from apes some hundreds of thousands of years ago and much further, so any evidence found to the contrary is ignored and tossed aside. A common example we will soon document is that articles and even human remains that are found in coal. As coal is considered quite old in the evolutionary scale of things, (often more than 200 million years), any such finding should controvert the entire premise of human evolution by huge epochs of time. Here I have included in a plethora of evidence in support the Flood account. As such, if the Flood (in strict adherence to the Biblical account) occurred, we should be able to enter the fields of Archaeology, Paleontology and Geology and find this obvious evidence.
The “Midland Man” Texas
was actually a female. In 1953, Keith Glasscock recovered artifacts and human remains in a grey sand “blow out” near Midland, TX. The finds were located below five layers of water deposited sediments, totaling nearly sixty feet of overburden (see The Noah Code p.. The skeletal remains, parts of a skull and two fragmentary ribs, are thought to be the oldest in North America. The location was named the Scharbauer site after the property owner. Remains of extinct antelope, horse, mammoth and bison were found with the subject. A number of arrow points were also recovered. Chemical analysis of the bones showed the human and animal remains were contemporary of each other. Here again we have a sedimentary waterborne deposit, containing human remains, found to be buried at a time period closely associated with other such finds in North America. In addition, the team mentioned that the skull was of the elongated type, as found in other Texas excavations buried catastrophically in water borne tombs.Also in Texas, skeletons with very long, narrow heads were unearthed in number. The subject was of considerable study and comment by Hooton, 1933; Roberts, 1945; and Woodbury, 1935. The remains were found in deeply buried silts (water deposits), but are little mentioned or publicized.
(Wormington Ancient Man in North America 1957)
was actually a female. In 1953, Keith Glasscock recovered artifacts and human remains in a grey sand “blow out” near Midland, TX. The finds were located below five layers of water deposited sediments, totaling nearly sixty feet of overburden (see The Noah Code p.. The skeletal remains, parts of a skull and two fragmentary ribs, are thought to be the oldest in North America. The location was named the Scharbauer site after the property owner. Remains of extinct antelope, horse, mammoth and bison were found with the subject. A number of arrow points were also recovered. Chemical analysis of the bones showed the human and animal remains were contemporary of each other. Here again we have a sedimentary waterborne deposit, containing human remains, found to be buried at a time period closely associated with other such finds in North America. In addition, the team mentioned that the skull was of the elongated type, as found in other Texas excavations buried catastrophically in water borne tombs.Also in Texas, skeletons with very long, narrow heads were unearthed in number. The subject was of considerable study and comment by Hooton, 1933; Roberts, 1945; and Woodbury, 1935. The remains were found in deeply buried silts (water deposits), but are little mentioned or publicized.
(Wormington Ancient Man in North America 1957)
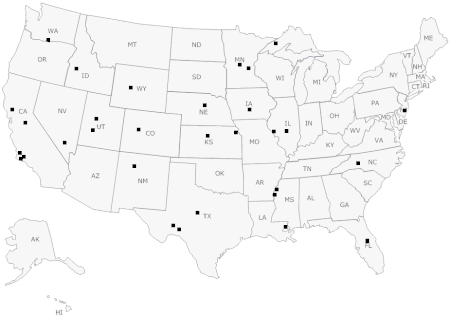 Deeply buried finds of human remains exist across North America
Deeply buried finds of human remains exist across North America
Human Remains in 1840 Table Mountain CA, Gold mine finds
Wright, Frederick G. Science 20:275-27 1892
In February 1866, a skull was removed by one Mr. Mattison, in Calaveras County from a layer of gravel 130 feet below the surface. Later a human jaw, also inspected by J. D. Whitney, State geologist at that time who researched its location and authenticity. The jaw was given to a Dr. Snell by miners, who stated it came from the gravels beneath the lava cap at Table Mountain in Tuolumne County, CA. Noted geologists Mr. George H. Baker, Mr. King along with Professor Marsh, Professor Putnam and W. H. Dall attested to the fact that the Calaveras skull was found in place beneath a stream of gravel in the Table formation beneath this same stream of lava. Their position indicates they were over 30 million years old, in modern terms.
Speaking about the Whitney papers on these finds; in August, 1879, AAAS President and foremost paleontologist O. C. Marsh, stated: “The proof offered on this point by Professor J. D. Whitney in his recent work (Aurif. Gravels of Sierra Nevada) is so strong, and his careful, conscientious method of investigation so well known, that his conclusions seem irresistible. At present, the known facts indicate that the American beds containing human remains and works of man, are as old as the Pliocene of Europe. The existence of man in the Tertiary period seems now fairly established.”[i]
Human Skull Found at Stanford, Menlo Park, CA
While excavating for a building project, scientists from Stanford discovered mastodon remains 22 feet below ground level near the campus. The observing scientists recalled an earlier find of a modern human skull found by Bruce Seymour, a Stanford University student, who found this skull twenty feet below the surface in the bank of San Francisquito Creek, at the same depth and strata of the Mastodon. The skull was cemented in a gravel stratum on which an alluvial cone had been formed. Bailey Willis (a competent geologist that had worked closely with Hrdlicka*) visited the locality, and determined that a considerable period of time must have been required for the formation of the alluvial cone which overlay the gravel, and for the cutting of the present creek bed. He suggested that the skull might have been deposited more than 4,000 years ago. According to Wormington, Willis is a capable geologist, likely to be “extremely cautious in supporting claims for the antiquity of human remains.” (Wormington 1957) The skull, which was studied by T. D. McCown (see Early Man in the New World, 1950) deter- mined it was a “male between thirty-five and forty-five years old.” The phys- ical and chemical condition of the specimen made it appear unlikely that it could be very recent. Researchers discussing the implications quoted Dr.
J.W. Gidley as stating: “If this mastodon is of the late Miocene or early Pliocene as D. Blackwelder says it is, that sets it (the skull) back some two or three million years. And we have no evidence man has been here that long.”
The Noah Code Rose, M. p. 279, 80 Quoting from Science, 69 Feb. 1, 1929
Los Angeles Skeletons
In 1914, a complete human skeleton, animal bones and artifacts were found in a Los Angeles area tar pit. Later in 1924, at Angeles Mesa, six skeletons were found (Heizer, 1950) at depths of nineteen to twenty-three feet below the surface. Later, more finds surfaced as part of the excavation in 1936 when workmen were digging a storm drain beneath the Los Angeles River. This find revealed more human bones, including a partial human cranium and seven fragments of other bones at depths of twelve to thirteen feet below grade. The bones and cranium were mineralized and coated heavily with sandstone and conglomerate. Extinct animal bones were also discovered two months later in the same stratum. A. Lopatin, of the University of Southern California excavated two teeth later identified as those from an Imperial Mammoth. The geologic study of the associated stratum was con- ducted by Thomas Clements, a well known geologist who concluded they were of Pleistocene age.
Ref. Rose, M. The Noah Code p. 284 Quoting Wormington, Hannah 1957 Ancient Man in North America
Note; Wormington was subsequently fired as curator of archeology at the Denver Museum shortly after publishing this volume.
Torrington, Wyoming
Four skeletons were discovered near Torrington, Wyoming, according to W. W. Howells (1938). The skeletons closely resemble those found at Lake Pelican. Unfortunately these bones were found during blasting activities but apparently were entombed in a sealed cave opened in the excavation process. Upon further investigation, the remains were determined to be that of an adult male, two females of differing ages, and an infant. It was stated that the remains and artifacts resembled many other such finds across the continent in their condition of covering and ethnicity.
New Orleans Man
The original report on this find, usually credited to D. B. Dowler, is by Prof. D. Drake, reads as follows: “In 1844, I visited two gas tanks, each 60 feet in diameter and 16 feet deep, recently sunk in the back part of the city [i. e., New Orleans] and received from the intelligent superintendent, Doctor Rogers, an account of what was met with in excavating them. At first they encountered soil and soft river mud, then harder laminated blue alluvion, then deep black mold resting on wet bluish quicksand. The roots and the basis or stumps of no fewer than four successive growths (or stacks) of trees, apparently cypress, were found standing at different elevations. The first had a diameter of 2 feet 6 inches, the second of 6 feet, the third of 4 feet, and the fourth of 12 feet, at a short distance up, with a base of 28 feet for the roots. It is embedded in a soft deep-black mold. When cut with the spade much of this wood resembled cheese in texture, but hardened on drying. At the depth of 7 and 16 feet burnt wood was met with. No shells or bones of land animals or fish were observed, but in a tank previously excavated, at the depth of 16 feet the skeleton of a man was found. The cranium lay between the roots of a tree and was in a tolerable state of preservation, but most of the other bones crumbled on pressure. A small ossilium, which I saw, indicated the female sex.*
*Note: A similar “buried forest” is found near the shores of New Jersey, where for years loggers extracted the timbers of huge trees flattened to horizontal from some earlier watery catastrophe. Such buried forests also exist along the central Oregon coast near Pacific City and others were unearthed in a recent excavation along Hwy 20. These were c14 dated <40,000 years old.
Lyell, Mississippi Find and the Bias
Charles Lyell first visited this country in 1850 and witnessed with his own eyes (to his consternation) the recovery of human remains 30 feet below the surface in association with extinct animals, just as in hundreds of locations across Europe! Speaking of the discovery, Lyell records: “It appeared to be the bone of a man, in the same state of preservation, and was of the same dark color as the other fossils, and was believed to have come like them from a depth of about thirty feet from the surface.”
Lyell goes on to urge that until other like specimens could be found, this case must be overlooked. He rationalizes the site as possibly that of a native graveyard. At this juncture it’s worthwhile to quote the presiding witness who made the discovery in the first place, Dr. Dickeson. Documenting this find in contradiction to Lyell’s comments, Dickeson stated the human re- mains were taken from a uniform and undisturbed bed of blue clay, two feet below the skeletons of the megalonyx (mastodon) and other extinct quadrupeds. The discoverer tells us: “The bone is that of a young man of about sixteen years of age, as determined by its size and form. That this bone is strictly in the fossil state, is manifest from its physical characters, in which it accords in every respect of color, density, with those of the megalonyx and other associated bones. That it could not have drifted into the position in which it was found is manifest from several facts: 1) the plateau of blue clay is not appreciably acted upon by those causes that produce ravines in the superincum bent diluvium, 2) That the human bone was found at least two feet below three associated skeletons of the megalonyx, all of which, judging from the apposition or proximity of their several parts, had been de- posited in this locality. And lastly, because there was no admixture of diluvial drift with the blue clay, which latter retains its homogeneous character equally in the higher part that furnished extinct quadrupeds, and in its lower part that contained the remains of man.”
The Noah Code 2017, p. 245-6
The Soda Bar Colorado Find
Soon after Lyell’s visit to America, miners discovered human remains twenty-two feet below the surface in the Soda Bar Colorado gold mines in 1860.* The skeletal remains were found lying facedown beneath gravel and boulders in the rocky deposits at Soda Bar, high in the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Still intact were the larger bones and skull, found to be fully modern. Witnessing the find, Mr. L. Berthond,* reported to the Academy of Science at Philadelphia in 1866: “[it] was a point conclusively shown, namely, that prior to the cause which covered Soda Hill, Soda Bar, and Dry Diggings Hill with its enormous beds of gravel, sand and boulders, and its native gold, man roved and dwelt in this region.” Along with the bones a pine tree was found two feet beneath in strata called “red rock.” The tree observed had its bark charred and disintegrated upon contact with the air. It would not be a stretch to surmise the tree was exposed to tremendous heat, then covered by sediments carried by moving water, nor to guess that the body was deposited then covered by the water transported gravel and boulders. Hence this find represents yet another important discovery conveniently omitted from the modern literature.
*Berthond concluded: “We confess that our preconceived notions of the antiquity of this Globe have received a severe shock by this discovery, and have modified our views as to the antiquity of the strata in this part of the Globe in this part of the continent…”
Divide Found in New Mexico
At the Sandra Cave in the Las Huertas Canyon, New Mexico, were found a variety of man-made implements together with the fossil remains of such animals as the horse, camel, bison, mammoth, ground sloth, and wolf. The cave was initially discovered by treasure hunters on the lower slope of Bishops Cap, the principal a Mr. Roscoe Conkling of El Paso, TX. Intrigued by its soft floor, a party was formed and returned to the site along with an expert witness. Excavations commenced in the presence of a recognized authority, Mr. William Bryan, invited to be on hand to witness any potential fossils of importance and to verify the geological sequence of the excavation. Digging down through the layers, bones of animals now extinct began to be exposed and removed. To the shock of all present, suddenly a human skull cap appeared at the 12 foot level. Further down in the water deposited sediment layers, a hard sandstone lens was encountered. When this layer was broken through, another skull was found, along with remains of other animals including a camel at nearly 21 feet in depth. Several archaeologists commented that this finding was of national significance, but for one reason or another, Bryan’s impressive report* never made it into the textbooks or literature and was sidelined into obscurity.
*Bryan, William Alanson; Science, 70:39-41 1929 New Mexico
Group of artifacts found in France
Jacques-Louis, Comte de Bournon (1751 – 1825) of France was a soldier and scientist who gained prominence in the British scientific community and was elected a fellow of the Royal and Geological Society. He was present when this discovery was made in a stone quarry used for rebuilding the Palace of Justice in Paris.
"The stone was a limestone of deep grey, and of that kind which are tender when they come out of the quarry, but harden by exposure to the air. The first which were wrought presented no appearance of any foreign bodies, but, after the workmen had removed the ten first beds, they were astonished, when taking away the eleventh, to find its inferior surface, at the depth of forty or fifty feet, covered with shells. The stone of this bed having been removed, ..they found stumps of columns and fragments of stone half wrought, and the stone was exactly similar to that of the quarry: they found moreover coins, handles of hammers, and other tools or fragments of tools in wood. But that which principally commanded their attention, was a board about one inch thick and seven or eight feet long; it was broken into many pieces, ..which was that of the boards of the same kind used by the masons and quarry men: it was worn in the same manner, rounded and waving upon the edges.” "Here then, we have the traces of a work executed by the hand of man, placed at a depth of fifty feet, and covered with eleven beds of compact limestone: everything tended to prove that this work had been executed upon the spot where the traces existed. The presence of man had then preceded the formation of this stone, and that very considerably since he was already arrived at such a degree of civilization that the arts were known to him, and that he wrought the stone and formed columns out of it.”
American Journal of Science, 1820
Human marks in another stone quarry
In November 1830, two individual letter shapes were found extruded into a slab of marble 12 miles northwest of Philadelphia. In the normal course of business a marble block of 30 cubic feet was removed and taken to a sawing facility. When the workers noticed letters inset into this slab they thought virgin, they set the block aside and called in witnesses. The rough cut was taken from a depth of sixty to eighty feet deep in the pit.
Browne, J.B. American Journal of Science 1:19:361 1831.
Nail in "Ancient" Sandstone
In a Scotland, at a sandstone quarry a report was made that a nail was found set in a block of sandstone. The relic was found in stone dated 360 and 408 million years old. The principal who made the find, David Brewster was a famous Scottish physicist and founder of the British Association for the Advancement of Science. Brewster stated: “The stone in Kingoodie quarry consists of alternate layers of hard stone and a soft clayey substance called ‘till’; the courses of stone vary from six inches to upwards of six feet in thickness. The particular block in which the nail was found, was nine inches thick, and in proceeding to clear the rough block for dressing, the point of the nail was found projecting about half an inch (quite eaten with rust) into the ‘till,’ the rest of the nail lying along the surface of the stone to within an inch of the head, which went right down into the body of the stone.”
Brewster, David: Report of the British Association pt. 2, 51 1844
Iron pot found in coal:
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. Forbidden Archeology 2011. P. 806
Robert Nordling states; "While I was working in the Municipal Electric Plant in Thomas, Okla. in 1912, I came upon a solid chunk of coal which was too large to use. I broke it with a sledge hammer. This iron pot fell from the center, leaving the impression or mold of the pot in the piece of coal. Jim Stall (an employee of the company) witnessed the breaking of the coal, and saw the pot fall out. I traced the source of the coal, and found that it came from the Wilburton, Oklahoma, Mines.” Wilburton area coal is said to be over 300 million years old using uniform geologic tables.
Shoes in Stone
“Mystery of the Petrified ‘Shoe Sole’ 5,000,000 Years Old,” by Dr. W. H. Ballou. DR. Ballou wrote: “Some time ago, while he was prospecting for fossils in Nevada, John T. Reid, a distinguished mining engineer and geologist, stopped suddenly and looked down in utter bewilderment and amazement at a rock near his feet. For there, a part of the rock itself, was what seemed to be a human footprint! Closer inspection showed that it was not a mark of a naked foot, but was, apparently, a shoe sole which had been turned into stone". The Triassic rock bearing the fossil shoe sole is now recognized as being more than 200 million years old. Mr. Reid took the specimen to the American Museum of Natural History where the expert staff seemed amazed, a report was written but when inquired of later it could not be found. The sole imprint was so clear a wear spot was visible a the heal pressure point. The artifact has been left a mystery to secular scientists, but not to those who hold the Bible authoritative.
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. Forbidden Archeology 2011. p. 807-8
Sole print including trilobites, the Meister Story
Corless William R. Handbook of Geological Enigma's Sourcebook Project 1980 p. 642
William Meister was collecting trilobites near Antelope Springs, Utah. Upon breaking open a clast rock the two parts fell open and there before his eyes were the impression of shoe soles impregnated with trilobites, an animal dated back 500 million years! Geologist after geologist has studied the imprints and rejected them due to the geologic location of trilobite's, which contradict the evolution chart of origins. One geologist familiar with the area visited the site and reported that surface rocks existed of the same nature of the one found, so Meister was exonerated from any kind of fraud. One geologist admitted that he "could not accept it", and added that; no geologist would.
Fossil human-like footprints.
Corless Handbook of Geological Enigma's Sourcebook Project 1980 p. 668-9
Professor W. G. Burroughs, head of the department of geology at Berea College in Berea, Kentucky, reported in 1938 that he had identified a number of prints in the vicinity for years. Human and human mixed with animal prints have been known to be found in Australia, Dakota, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Massachusetts , Nevada, S Louis, Mo. Texas and Turkey.
Heidelberg Mandible
Dr. Otto Schoetensack, lecturer on Geology in the University of Heidelberg, often visited a fossil rich deposit in a gravel pit near the institution. After waiting and searching for twenty years, the owner of the pit, Herr J. Rosch, was able to inform him on October 21st, 1907, that his twenty years search had at last been realized. "Yesterday" he wrote, "the desired evidence was obtained, for 20 m. below the surface soil, and above the floor of my sand-pit, there was found the lower jaw of primitive man, in good preservation, and with all its teeth." Concerning the authenticity of the find there cannot be any doubt; the bed in which the mandible was covered by a series of deposits, amounting in all to 78 feet, over the mandible Dr. Schoetensack recognized twenty four different strata containing. They fall into three series - the uppermost, formed by recent loess a fine earth, a product of floods and drought; (2) the ancient loess a sandy loam, also a deposit from muddy waters; (3) the Mauer sands. In one of the lower strata of this series the mandible was found. In the lower strata, remains of the following extinct animals were found: " the lion, an extinct form of cat, a dog, two forms of bear, a species of bison, an early Pleistocene form of horse, and an early form of rhinoceros… "These are not primitive or simian characters, but the reverse; they are modifications confined, so far as we have yet discovered, to this peculiar variety or species of man."
"No revelation of prehistoric man could be more convincing than the discovery of the Heidelberg mandible. We have no shadow of doubt as to its authenticity or significance." So states Arthur Kieth in The Antiquity of Man. 1915. 233-4
Galley Hill, England
Keith, Arthur. The Antiquity of Man. 1915.
In 1888, workmen removing deposits at Galley Hill, near London, England, an exposed a fully modern human remains above a bed of chalk. The overlying layers were about 10 or 11 feet thick. Here was discovered a human skeleton firmly embedded in these deposits about 8 feet below the surface. A qualified observer determined this locale was not a burial site: “No doubt could possibly arise to the observation of an ordinary intelligent person of their deposition contemporaneously with that of the gravel. This undisturbed state of the stratum was so palpable to the workman that he said, ‘The man or animal was not buried by anybody.’” Numerous tools were also recovered from the Galley Hill site and surrounding area.
Clichy Skeleton In 1868
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. (2011-01-30). The Hidden History of the Human Race
As documented to the Anthropological Society of Paris , one Eugene Bertrand claimed that he found parts of a human skull, along with a femur, tibia, and some foot bones, in a quarry near Avenue de Clichy. The bones were found 16+ feet beneath the surface. This layer was the same age in Geology terms as the Galley Hill skeleton was discovered. This would make the Clichy bones approximately 330,000 years old.
La Denise Skull Fragments
La Denise, France In the 1840’s, pieces of human bone were discovered in the midst of volcanic strata, including a forehead section. Sir Arthur Keith wrote; “differs in no essential particular from the frontal bone of a modern skull.” The remains were found between two layers of lava. The first lava layer was from the Pliocene and the last from the Late Pleistocene, or up to 2 million years old.
From Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. (2011-01-30). The Hidden History of the Human Race
Buenos Aires Skull
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. (2011-01-30). The Hidden History of the Human Race.
A very strong case for anatomically modern humans existing in very early times comes from Argentina. In 1896, workers excavating a dry dock in Buenos Aires uncovered a skull in a layer referred to as “the upper-most portion of the Pre-Ensenadean stratum.” Placing the remains over 1 million years old as measured by evolution based timelines, far to old for the existence of modern man.
Foxall Jaw
From Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. (2011-01-30). The Hidden History of the Human Race. In 1855, a human jaw was discovered at Foxhall, England, by workers digging in a quarry 16 feet below the surface. Collyer determined that this specimen was; “the oldest relic of the human animal in existence.” Artifacts were also uncovered in the same strata, over 2 million years dated by uniform means. Collyer was ecstatic about this find and presented it to the various authorities of the day including Thomas Huxley, Richard Owen and Charles Lyell. Huxley related that in his opinion the piece; “did not indicate it belonged to an extinct or aberrant race of mankind.” Others were skeptical.
The Castenedolo finds
Keith, Arthur. The Antiquity of Man. 1915. Chap XIII
Late in 1860, one Giuseppe Ragazzoni, a geologist at Brescia, visited the area of Castenedolo, “Searching along a bank of coral for shells, there came into my hand the top portion of a cranium, completely filled with pieces of coral cemented with the blue-green clay characteristic of that formation. Astonished, I continued the search, and in addition to the top portion of the cranium I found other bones of the thorax and limbs, which quite apparently belonged to an individual of the human species.” Later he recovered more "modern" human fossils, to the astonishment of the world, including a man, women and two children. This finding was suppressed and has found little publicity as the layers, all water deposited, dated over 4 MY as determined by uniform geologic means. Giuseppe Sergi, famous anatomist of Rome, visited Ragazzoni in 1883 and verified the remains of the four individuals, an adult male, female, and two children. A noted authority of the day, Sergi believed the Castenedolo skeletons were authentic. As the skeptical reactions flowed in from others, he later said: “The tendency to reject, by reason of theoretical preconceptions, any discoveries that can demonstrate a human presence in the Tertiary is, I believe, a kind of scientific prejudice. Natural science should be stripped of this prejudice.” Later Sergi wrote: “By means of a despotic scientific prejudice, call it what you will, every discovery of human remains in the Pliocene has been discredited.”
The Honest end of Castenedolo
From Macalister’s Textbook of European Archaeology, 1921. Cambridge University Press.
Macalister mentions the Castenedolo finds “whatever we may think of them, have to be treated seriously.” Further he comments;“unearthed by a competent geologist, Ragazzoni and examined by a competent anatomist, Sergi.” He unknowingly predicts; “there must be something wrong somewhere.” “Now, if they really belonged to the stratum in which they were found,”…“this would imply an extraordinarily long standstill for evolution. It is much more likely that there is something amiss with the observations.” Finally and honestly asserting: “The acceptance of a Pliocene date for the Castenedolo skeletons would create so many insoluble problems that we can hardly hesitate in choosing between the alternatives of adopting or rejecting their authenticity.”
Savona Italy, Skeleton
Around 1850 while excavating for a Church in Savona, Italy, a fully modern human skeleton was unearthed 10 feet below the grade in a layer thought to be “millions” of years in geologic age -(geologists of the day put the age the layer over 3 million years old, again assuming uniform evolutionary geology was correct). The presenter of the find, Arthur Issel observed; “The body was discovered in an outstretched position, with the arms extending forward, the head slightly bent forward and down, the body very much elevated relative to the legs, like a man in the water." Animal bones were found scattered with the human remains in the same layer. As this skeleton appeared to be washed in by water, face down and trapped against the side of rock, this condition supports the find as but none other than a remnant the great flood, 75 miles inland.
Human skull found at Stanford, Menlo Park, CA
Science, 69: suplii, Feb, 1 1929, from Corliss, William R. Handbook of Geological Enigma's Sourcebook Project 1980 p. 673
Discovering mastodon remains 22 feet below ground level near the campus, the observing scientists recalled a little reported earlier find of a modern human skull found nearby at same depth in the same strata. Three researchers are quoted discussing the implications. One, a Dr. J.W. Gidley is quoted as stating, "If this mastodon is of the late Miocene are early Pliocene as D. Blackwelder says it is, that sets it (the skull) back some two or three million years. And we have no evidence man has been here that long."
Switzerland
According to Gabriel de Mortillet, M. Quiquerez reported the discovery of a skeleton at Delémont in Switzerland in clays (water deposits) in the Eocene time – at least 39 million years old on the Geologic chart.
US Coal Man
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. Forbidden Archaeology Torchlight Press 2011 p. 454
In December of 1862, The Geologist reported: “In Macoupin County, Illinois, the bones of a man were recently found on a coal-bed capped with two feet of slate rock, ninety feet below the surface of the earth. The bones, when found, were covered with a crust or coating of hard glossy matter, as black as coal itself, but when scraped away left the bones white and natural.” The coal in which the Macoupin County skeleton was a layer claimed to be over 280 million years of age on the geologic chart.
Reck’s Skeleton
In 1913, Professor Hans Reck of Berlin University, conducted investigations in the now famous graveyard at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania. Seeing a protrusion, one of his companions noticed portions of a skeleton embedded in the rock. The workers labored to extract the remains out of the stone with hammers and chisels. This fully modern human was located in a layer far too "old". by evolution standards that have modern man coming on the scene 200,000 years ago.
In spite of all the evidence to the contrary, modern analysts confidently assert Reck’s Skeleton was of recent burial. It's rarely mentioned the records. The possibility of modern skeletons in such supposedly ancient strata is very destructive to modern scientific thought. Reck’s find is significant, it exposes the bias of the "science" of human origins, even 100 years past. Finds such as this undermine the long ages theory of Darwinian evolution, upon which modern anthropology, archeology and long-age geology origins theories are based.
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. Forbidden Archaeology Torchlight Press 2011
New Mexico - Human Bones in Cavern
Bryan, William Alanson; Science, 70:39-41 1929
A cave was discovered by local treasure hunters on the lower slope of Bishops Cap by a Mr. Roscoe Conkling of El Paso in the 1920's. Intrigued by its soft floor, a party was formed and excavations began in the presence of a recognized authority able to witness any potential unearthing of items of importance. Digging down through the layers, animal bones now extinct began to be exposed and removed, then suddenly a human skull cap appeared at the 12 foot level. Further down the sediment layers a hard lens was encountered, and when broken through was found another skull and remains of numerous other animals including a camel at nearly 21 feet in depth. The scientist commented that this finding was of national significance, but for one reason or another, it never got into the textbooks.
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. Forbidden Archaeology Torchlight Press 2011 p.444
Wright, Frederick G. Science 20:275-27 1892
In February 1866, a skull was removed by one Mr. Mattison, in Calaveras County from a layer of gravel 130 feet below the surface. Later a human jaw, also inspected by J. D. Whitney, State geologist at that time who researched its location and authenticity. The jaw was given to a Dr. Snell by miners, who stated it came from the gravels beneath the lava cap at Table Mountain in Tuolumne County, CA. Noted geologists Mr. George H. Baker, Mr. King along with Professor Marsh, Professor Putnam and W. H. Dall attested to the fact that the Calaveras skull was found in place beneath a stream of gravel in the Table formation beneath this same stream of lava. Their position indicates they were over 30 million years old, in modern terms.
Speaking about the Whitney papers on these finds; in August, 1879, AAAS President and foremost paleontologist O. C. Marsh, stated: “The proof offered on this point by Professor J. D. Whitney in his recent work (Aurif. Gravels of Sierra Nevada) is so strong, and his careful, conscientious method of investigation so well known, that his conclusions seem irresistible. At present, the known facts indicate that the American beds containing human remains and works of man, are as old as the Pliocene of Europe. The existence of man in the Tertiary period seems now fairly established.”[i]
Human Skull Found at Stanford, Menlo Park, CA
While excavating for a building project, scientists from Stanford discovered mastodon remains 22 feet below ground level near the campus. The observing scientists recalled an earlier find of a modern human skull found by Bruce Seymour, a Stanford University student, who found this skull twenty feet below the surface in the bank of San Francisquito Creek, at the same depth and strata of the Mastodon. The skull was cemented in a gravel stratum on which an alluvial cone had been formed. Bailey Willis (a competent geologist that had worked closely with Hrdlicka*) visited the locality, and determined that a considerable period of time must have been required for the formation of the alluvial cone which overlay the gravel, and for the cutting of the present creek bed. He suggested that the skull might have been deposited more than 4,000 years ago. According to Wormington, Willis is a capable geologist, likely to be “extremely cautious in supporting claims for the antiquity of human remains.” (Wormington 1957) The skull, which was studied by T. D. McCown (see Early Man in the New World, 1950) deter- mined it was a “male between thirty-five and forty-five years old.” The phys- ical and chemical condition of the specimen made it appear unlikely that it could be very recent. Researchers discussing the implications quoted Dr.
J.W. Gidley as stating: “If this mastodon is of the late Miocene or early Pliocene as D. Blackwelder says it is, that sets it (the skull) back some two or three million years. And we have no evidence man has been here that long.”
The Noah Code Rose, M. p. 279, 80 Quoting from Science, 69 Feb. 1, 1929
Los Angeles Skeletons
In 1914, a complete human skeleton, animal bones and artifacts were found in a Los Angeles area tar pit. Later in 1924, at Angeles Mesa, six skeletons were found (Heizer, 1950) at depths of nineteen to twenty-three feet below the surface. Later, more finds surfaced as part of the excavation in 1936 when workmen were digging a storm drain beneath the Los Angeles River. This find revealed more human bones, including a partial human cranium and seven fragments of other bones at depths of twelve to thirteen feet below grade. The bones and cranium were mineralized and coated heavily with sandstone and conglomerate. Extinct animal bones were also discovered two months later in the same stratum. A. Lopatin, of the University of Southern California excavated two teeth later identified as those from an Imperial Mammoth. The geologic study of the associated stratum was con- ducted by Thomas Clements, a well known geologist who concluded they were of Pleistocene age.
Ref. Rose, M. The Noah Code p. 284 Quoting Wormington, Hannah 1957 Ancient Man in North America
Note; Wormington was subsequently fired as curator of archeology at the Denver Museum shortly after publishing this volume.
Torrington, Wyoming
Four skeletons were discovered near Torrington, Wyoming, according to W. W. Howells (1938). The skeletons closely resemble those found at Lake Pelican. Unfortunately these bones were found during blasting activities but apparently were entombed in a sealed cave opened in the excavation process. Upon further investigation, the remains were determined to be that of an adult male, two females of differing ages, and an infant. It was stated that the remains and artifacts resembled many other such finds across the continent in their condition of covering and ethnicity.
New Orleans Man
The original report on this find, usually credited to D. B. Dowler, is by Prof. D. Drake, reads as follows: “In 1844, I visited two gas tanks, each 60 feet in diameter and 16 feet deep, recently sunk in the back part of the city [i. e., New Orleans] and received from the intelligent superintendent, Doctor Rogers, an account of what was met with in excavating them. At first they encountered soil and soft river mud, then harder laminated blue alluvion, then deep black mold resting on wet bluish quicksand. The roots and the basis or stumps of no fewer than four successive growths (or stacks) of trees, apparently cypress, were found standing at different elevations. The first had a diameter of 2 feet 6 inches, the second of 6 feet, the third of 4 feet, and the fourth of 12 feet, at a short distance up, with a base of 28 feet for the roots. It is embedded in a soft deep-black mold. When cut with the spade much of this wood resembled cheese in texture, but hardened on drying. At the depth of 7 and 16 feet burnt wood was met with. No shells or bones of land animals or fish were observed, but in a tank previously excavated, at the depth of 16 feet the skeleton of a man was found. The cranium lay between the roots of a tree and was in a tolerable state of preservation, but most of the other bones crumbled on pressure. A small ossilium, which I saw, indicated the female sex.*
*Note: A similar “buried forest” is found near the shores of New Jersey, where for years loggers extracted the timbers of huge trees flattened to horizontal from some earlier watery catastrophe. Such buried forests also exist along the central Oregon coast near Pacific City and others were unearthed in a recent excavation along Hwy 20. These were c14 dated <40,000 years old.
Lyell, Mississippi Find and the Bias
Charles Lyell first visited this country in 1850 and witnessed with his own eyes (to his consternation) the recovery of human remains 30 feet below the surface in association with extinct animals, just as in hundreds of locations across Europe! Speaking of the discovery, Lyell records: “It appeared to be the bone of a man, in the same state of preservation, and was of the same dark color as the other fossils, and was believed to have come like them from a depth of about thirty feet from the surface.”
Lyell goes on to urge that until other like specimens could be found, this case must be overlooked. He rationalizes the site as possibly that of a native graveyard. At this juncture it’s worthwhile to quote the presiding witness who made the discovery in the first place, Dr. Dickeson. Documenting this find in contradiction to Lyell’s comments, Dickeson stated the human re- mains were taken from a uniform and undisturbed bed of blue clay, two feet below the skeletons of the megalonyx (mastodon) and other extinct quadrupeds. The discoverer tells us: “The bone is that of a young man of about sixteen years of age, as determined by its size and form. That this bone is strictly in the fossil state, is manifest from its physical characters, in which it accords in every respect of color, density, with those of the megalonyx and other associated bones. That it could not have drifted into the position in which it was found is manifest from several facts: 1) the plateau of blue clay is not appreciably acted upon by those causes that produce ravines in the superincum bent diluvium, 2) That the human bone was found at least two feet below three associated skeletons of the megalonyx, all of which, judging from the apposition or proximity of their several parts, had been de- posited in this locality. And lastly, because there was no admixture of diluvial drift with the blue clay, which latter retains its homogeneous character equally in the higher part that furnished extinct quadrupeds, and in its lower part that contained the remains of man.”
The Noah Code 2017, p. 245-6
The Soda Bar Colorado Find
Soon after Lyell’s visit to America, miners discovered human remains twenty-two feet below the surface in the Soda Bar Colorado gold mines in 1860.* The skeletal remains were found lying facedown beneath gravel and boulders in the rocky deposits at Soda Bar, high in the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Still intact were the larger bones and skull, found to be fully modern. Witnessing the find, Mr. L. Berthond,* reported to the Academy of Science at Philadelphia in 1866: “[it] was a point conclusively shown, namely, that prior to the cause which covered Soda Hill, Soda Bar, and Dry Diggings Hill with its enormous beds of gravel, sand and boulders, and its native gold, man roved and dwelt in this region.” Along with the bones a pine tree was found two feet beneath in strata called “red rock.” The tree observed had its bark charred and disintegrated upon contact with the air. It would not be a stretch to surmise the tree was exposed to tremendous heat, then covered by sediments carried by moving water, nor to guess that the body was deposited then covered by the water transported gravel and boulders. Hence this find represents yet another important discovery conveniently omitted from the modern literature.
*Berthond concluded: “We confess that our preconceived notions of the antiquity of this Globe have received a severe shock by this discovery, and have modified our views as to the antiquity of the strata in this part of the Globe in this part of the continent…”
Divide Found in New Mexico
At the Sandra Cave in the Las Huertas Canyon, New Mexico, were found a variety of man-made implements together with the fossil remains of such animals as the horse, camel, bison, mammoth, ground sloth, and wolf. The cave was initially discovered by treasure hunters on the lower slope of Bishops Cap, the principal a Mr. Roscoe Conkling of El Paso, TX. Intrigued by its soft floor, a party was formed and returned to the site along with an expert witness. Excavations commenced in the presence of a recognized authority, Mr. William Bryan, invited to be on hand to witness any potential fossils of importance and to verify the geological sequence of the excavation. Digging down through the layers, bones of animals now extinct began to be exposed and removed. To the shock of all present, suddenly a human skull cap appeared at the 12 foot level. Further down in the water deposited sediment layers, a hard sandstone lens was encountered. When this layer was broken through, another skull was found, along with remains of other animals including a camel at nearly 21 feet in depth. Several archaeologists commented that this finding was of national significance, but for one reason or another, Bryan’s impressive report* never made it into the textbooks or literature and was sidelined into obscurity.
*Bryan, William Alanson; Science, 70:39-41 1929 New Mexico
Group of artifacts found in France
Jacques-Louis, Comte de Bournon (1751 – 1825) of France was a soldier and scientist who gained prominence in the British scientific community and was elected a fellow of the Royal and Geological Society. He was present when this discovery was made in a stone quarry used for rebuilding the Palace of Justice in Paris.
"The stone was a limestone of deep grey, and of that kind which are tender when they come out of the quarry, but harden by exposure to the air. The first which were wrought presented no appearance of any foreign bodies, but, after the workmen had removed the ten first beds, they were astonished, when taking away the eleventh, to find its inferior surface, at the depth of forty or fifty feet, covered with shells. The stone of this bed having been removed, ..they found stumps of columns and fragments of stone half wrought, and the stone was exactly similar to that of the quarry: they found moreover coins, handles of hammers, and other tools or fragments of tools in wood. But that which principally commanded their attention, was a board about one inch thick and seven or eight feet long; it was broken into many pieces, ..which was that of the boards of the same kind used by the masons and quarry men: it was worn in the same manner, rounded and waving upon the edges.” "Here then, we have the traces of a work executed by the hand of man, placed at a depth of fifty feet, and covered with eleven beds of compact limestone: everything tended to prove that this work had been executed upon the spot where the traces existed. The presence of man had then preceded the formation of this stone, and that very considerably since he was already arrived at such a degree of civilization that the arts were known to him, and that he wrought the stone and formed columns out of it.”
American Journal of Science, 1820
Human marks in another stone quarry
In November 1830, two individual letter shapes were found extruded into a slab of marble 12 miles northwest of Philadelphia. In the normal course of business a marble block of 30 cubic feet was removed and taken to a sawing facility. When the workers noticed letters inset into this slab they thought virgin, they set the block aside and called in witnesses. The rough cut was taken from a depth of sixty to eighty feet deep in the pit.
Browne, J.B. American Journal of Science 1:19:361 1831.
Nail in "Ancient" Sandstone
In a Scotland, at a sandstone quarry a report was made that a nail was found set in a block of sandstone. The relic was found in stone dated 360 and 408 million years old. The principal who made the find, David Brewster was a famous Scottish physicist and founder of the British Association for the Advancement of Science. Brewster stated: “The stone in Kingoodie quarry consists of alternate layers of hard stone and a soft clayey substance called ‘till’; the courses of stone vary from six inches to upwards of six feet in thickness. The particular block in which the nail was found, was nine inches thick, and in proceeding to clear the rough block for dressing, the point of the nail was found projecting about half an inch (quite eaten with rust) into the ‘till,’ the rest of the nail lying along the surface of the stone to within an inch of the head, which went right down into the body of the stone.”
Brewster, David: Report of the British Association pt. 2, 51 1844
Iron pot found in coal:
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. Forbidden Archeology 2011. P. 806
Robert Nordling states; "While I was working in the Municipal Electric Plant in Thomas, Okla. in 1912, I came upon a solid chunk of coal which was too large to use. I broke it with a sledge hammer. This iron pot fell from the center, leaving the impression or mold of the pot in the piece of coal. Jim Stall (an employee of the company) witnessed the breaking of the coal, and saw the pot fall out. I traced the source of the coal, and found that it came from the Wilburton, Oklahoma, Mines.” Wilburton area coal is said to be over 300 million years old using uniform geologic tables.
Shoes in Stone
“Mystery of the Petrified ‘Shoe Sole’ 5,000,000 Years Old,” by Dr. W. H. Ballou. DR. Ballou wrote: “Some time ago, while he was prospecting for fossils in Nevada, John T. Reid, a distinguished mining engineer and geologist, stopped suddenly and looked down in utter bewilderment and amazement at a rock near his feet. For there, a part of the rock itself, was what seemed to be a human footprint! Closer inspection showed that it was not a mark of a naked foot, but was, apparently, a shoe sole which had been turned into stone". The Triassic rock bearing the fossil shoe sole is now recognized as being more than 200 million years old. Mr. Reid took the specimen to the American Museum of Natural History where the expert staff seemed amazed, a report was written but when inquired of later it could not be found. The sole imprint was so clear a wear spot was visible a the heal pressure point. The artifact has been left a mystery to secular scientists, but not to those who hold the Bible authoritative.
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. Forbidden Archeology 2011. p. 807-8
Sole print including trilobites, the Meister Story
Corless William R. Handbook of Geological Enigma's Sourcebook Project 1980 p. 642
William Meister was collecting trilobites near Antelope Springs, Utah. Upon breaking open a clast rock the two parts fell open and there before his eyes were the impression of shoe soles impregnated with trilobites, an animal dated back 500 million years! Geologist after geologist has studied the imprints and rejected them due to the geologic location of trilobite's, which contradict the evolution chart of origins. One geologist familiar with the area visited the site and reported that surface rocks existed of the same nature of the one found, so Meister was exonerated from any kind of fraud. One geologist admitted that he "could not accept it", and added that; no geologist would.
Fossil human-like footprints.
Corless Handbook of Geological Enigma's Sourcebook Project 1980 p. 668-9
Professor W. G. Burroughs, head of the department of geology at Berea College in Berea, Kentucky, reported in 1938 that he had identified a number of prints in the vicinity for years. Human and human mixed with animal prints have been known to be found in Australia, Dakota, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Massachusetts , Nevada, S Louis, Mo. Texas and Turkey.
Heidelberg Mandible
Dr. Otto Schoetensack, lecturer on Geology in the University of Heidelberg, often visited a fossil rich deposit in a gravel pit near the institution. After waiting and searching for twenty years, the owner of the pit, Herr J. Rosch, was able to inform him on October 21st, 1907, that his twenty years search had at last been realized. "Yesterday" he wrote, "the desired evidence was obtained, for 20 m. below the surface soil, and above the floor of my sand-pit, there was found the lower jaw of primitive man, in good preservation, and with all its teeth." Concerning the authenticity of the find there cannot be any doubt; the bed in which the mandible was covered by a series of deposits, amounting in all to 78 feet, over the mandible Dr. Schoetensack recognized twenty four different strata containing. They fall into three series - the uppermost, formed by recent loess a fine earth, a product of floods and drought; (2) the ancient loess a sandy loam, also a deposit from muddy waters; (3) the Mauer sands. In one of the lower strata of this series the mandible was found. In the lower strata, remains of the following extinct animals were found: " the lion, an extinct form of cat, a dog, two forms of bear, a species of bison, an early Pleistocene form of horse, and an early form of rhinoceros… "These are not primitive or simian characters, but the reverse; they are modifications confined, so far as we have yet discovered, to this peculiar variety or species of man."
"No revelation of prehistoric man could be more convincing than the discovery of the Heidelberg mandible. We have no shadow of doubt as to its authenticity or significance." So states Arthur Kieth in The Antiquity of Man. 1915. 233-4
Galley Hill, England
Keith, Arthur. The Antiquity of Man. 1915.
In 1888, workmen removing deposits at Galley Hill, near London, England, an exposed a fully modern human remains above a bed of chalk. The overlying layers were about 10 or 11 feet thick. Here was discovered a human skeleton firmly embedded in these deposits about 8 feet below the surface. A qualified observer determined this locale was not a burial site: “No doubt could possibly arise to the observation of an ordinary intelligent person of their deposition contemporaneously with that of the gravel. This undisturbed state of the stratum was so palpable to the workman that he said, ‘The man or animal was not buried by anybody.’” Numerous tools were also recovered from the Galley Hill site and surrounding area.
Clichy Skeleton In 1868
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. (2011-01-30). The Hidden History of the Human Race
As documented to the Anthropological Society of Paris , one Eugene Bertrand claimed that he found parts of a human skull, along with a femur, tibia, and some foot bones, in a quarry near Avenue de Clichy. The bones were found 16+ feet beneath the surface. This layer was the same age in Geology terms as the Galley Hill skeleton was discovered. This would make the Clichy bones approximately 330,000 years old.
La Denise Skull Fragments
La Denise, France In the 1840’s, pieces of human bone were discovered in the midst of volcanic strata, including a forehead section. Sir Arthur Keith wrote; “differs in no essential particular from the frontal bone of a modern skull.” The remains were found between two layers of lava. The first lava layer was from the Pliocene and the last from the Late Pleistocene, or up to 2 million years old.
From Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. (2011-01-30). The Hidden History of the Human Race
Buenos Aires Skull
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. (2011-01-30). The Hidden History of the Human Race.
A very strong case for anatomically modern humans existing in very early times comes from Argentina. In 1896, workers excavating a dry dock in Buenos Aires uncovered a skull in a layer referred to as “the upper-most portion of the Pre-Ensenadean stratum.” Placing the remains over 1 million years old as measured by evolution based timelines, far to old for the existence of modern man.
Foxall Jaw
From Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. (2011-01-30). The Hidden History of the Human Race. In 1855, a human jaw was discovered at Foxhall, England, by workers digging in a quarry 16 feet below the surface. Collyer determined that this specimen was; “the oldest relic of the human animal in existence.” Artifacts were also uncovered in the same strata, over 2 million years dated by uniform means. Collyer was ecstatic about this find and presented it to the various authorities of the day including Thomas Huxley, Richard Owen and Charles Lyell. Huxley related that in his opinion the piece; “did not indicate it belonged to an extinct or aberrant race of mankind.” Others were skeptical.
The Castenedolo finds
Keith, Arthur. The Antiquity of Man. 1915. Chap XIII
Late in 1860, one Giuseppe Ragazzoni, a geologist at Brescia, visited the area of Castenedolo, “Searching along a bank of coral for shells, there came into my hand the top portion of a cranium, completely filled with pieces of coral cemented with the blue-green clay characteristic of that formation. Astonished, I continued the search, and in addition to the top portion of the cranium I found other bones of the thorax and limbs, which quite apparently belonged to an individual of the human species.” Later he recovered more "modern" human fossils, to the astonishment of the world, including a man, women and two children. This finding was suppressed and has found little publicity as the layers, all water deposited, dated over 4 MY as determined by uniform geologic means. Giuseppe Sergi, famous anatomist of Rome, visited Ragazzoni in 1883 and verified the remains of the four individuals, an adult male, female, and two children. A noted authority of the day, Sergi believed the Castenedolo skeletons were authentic. As the skeptical reactions flowed in from others, he later said: “The tendency to reject, by reason of theoretical preconceptions, any discoveries that can demonstrate a human presence in the Tertiary is, I believe, a kind of scientific prejudice. Natural science should be stripped of this prejudice.” Later Sergi wrote: “By means of a despotic scientific prejudice, call it what you will, every discovery of human remains in the Pliocene has been discredited.”
The Honest end of Castenedolo
From Macalister’s Textbook of European Archaeology, 1921. Cambridge University Press.
Macalister mentions the Castenedolo finds “whatever we may think of them, have to be treated seriously.” Further he comments;“unearthed by a competent geologist, Ragazzoni and examined by a competent anatomist, Sergi.” He unknowingly predicts; “there must be something wrong somewhere.” “Now, if they really belonged to the stratum in which they were found,”…“this would imply an extraordinarily long standstill for evolution. It is much more likely that there is something amiss with the observations.” Finally and honestly asserting: “The acceptance of a Pliocene date for the Castenedolo skeletons would create so many insoluble problems that we can hardly hesitate in choosing between the alternatives of adopting or rejecting their authenticity.”
Savona Italy, Skeleton
Around 1850 while excavating for a Church in Savona, Italy, a fully modern human skeleton was unearthed 10 feet below the grade in a layer thought to be “millions” of years in geologic age -(geologists of the day put the age the layer over 3 million years old, again assuming uniform evolutionary geology was correct). The presenter of the find, Arthur Issel observed; “The body was discovered in an outstretched position, with the arms extending forward, the head slightly bent forward and down, the body very much elevated relative to the legs, like a man in the water." Animal bones were found scattered with the human remains in the same layer. As this skeleton appeared to be washed in by water, face down and trapped against the side of rock, this condition supports the find as but none other than a remnant the great flood, 75 miles inland.
Human skull found at Stanford, Menlo Park, CA
Science, 69: suplii, Feb, 1 1929, from Corliss, William R. Handbook of Geological Enigma's Sourcebook Project 1980 p. 673
Discovering mastodon remains 22 feet below ground level near the campus, the observing scientists recalled a little reported earlier find of a modern human skull found nearby at same depth in the same strata. Three researchers are quoted discussing the implications. One, a Dr. J.W. Gidley is quoted as stating, "If this mastodon is of the late Miocene are early Pliocene as D. Blackwelder says it is, that sets it (the skull) back some two or three million years. And we have no evidence man has been here that long."
Switzerland
According to Gabriel de Mortillet, M. Quiquerez reported the discovery of a skeleton at Delémont in Switzerland in clays (water deposits) in the Eocene time – at least 39 million years old on the Geologic chart.
US Coal Man
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. Forbidden Archaeology Torchlight Press 2011 p. 454
In December of 1862, The Geologist reported: “In Macoupin County, Illinois, the bones of a man were recently found on a coal-bed capped with two feet of slate rock, ninety feet below the surface of the earth. The bones, when found, were covered with a crust or coating of hard glossy matter, as black as coal itself, but when scraped away left the bones white and natural.” The coal in which the Macoupin County skeleton was a layer claimed to be over 280 million years of age on the geologic chart.
Reck’s Skeleton
In 1913, Professor Hans Reck of Berlin University, conducted investigations in the now famous graveyard at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania. Seeing a protrusion, one of his companions noticed portions of a skeleton embedded in the rock. The workers labored to extract the remains out of the stone with hammers and chisels. This fully modern human was located in a layer far too "old". by evolution standards that have modern man coming on the scene 200,000 years ago.
In spite of all the evidence to the contrary, modern analysts confidently assert Reck’s Skeleton was of recent burial. It's rarely mentioned the records. The possibility of modern skeletons in such supposedly ancient strata is very destructive to modern scientific thought. Reck’s find is significant, it exposes the bias of the "science" of human origins, even 100 years past. Finds such as this undermine the long ages theory of Darwinian evolution, upon which modern anthropology, archeology and long-age geology origins theories are based.
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. Forbidden Archaeology Torchlight Press 2011
New Mexico - Human Bones in Cavern
Bryan, William Alanson; Science, 70:39-41 1929
A cave was discovered by local treasure hunters on the lower slope of Bishops Cap by a Mr. Roscoe Conkling of El Paso in the 1920's. Intrigued by its soft floor, a party was formed and excavations began in the presence of a recognized authority able to witness any potential unearthing of items of importance. Digging down through the layers, animal bones now extinct began to be exposed and removed, then suddenly a human skull cap appeared at the 12 foot level. Further down the sediment layers a hard lens was encountered, and when broken through was found another skull and remains of numerous other animals including a camel at nearly 21 feet in depth. The scientist commented that this finding was of national significance, but for one reason or another, it never got into the textbooks.
Cremo, Michael A.; Thompson, Richard L. Forbidden Archaeology Torchlight Press 2011 p.444
 Human bone excavated by Tournal, 1833. A few of hundreds from many caves
Human bone excavated by Tournal, 1833. A few of hundreds from many caves
Tournal’s 1833 Call for Reason - too many people in the caves..what were they hiding from?
Quoting M. Tournal’s works of 1833, Professor Fairholme tells us in 1840, p. 41: “[The] French geologists were so powerfully struck with the mixture of human and other bones, in some of the caves in the south of France, that a more strict scrutiny was instituted; and the results were published in a paper by M. Tournal, jun., of Narbonne, in No. 52 of Annates de Chimte et de Physique, from which the following is a short extract: In speaking of human remains, M. Tournal says, “The heads of the geological world would have it that they were, in all cases, recent, and accidental; and their opinions had the effect of deciding the point as a subject unworthy of further discussion. However, the discovery of the caves of Aude, of Herault, and of Gard, in the south of France, offers to the observer a crowd of human bones, and of ancient pottery, mixed up in the very same mud with those of hyenas, tigers, lions, stags, and a number of other animals of lost kinds. Attention was, therefore, again called to the subject, and MM. Marcel de Serres, Jules de Christol, and myself, after an attentive and conscientious examination, have come to the conclusion, that all these objects are of the same date, and, con- subsequently, that man was contemporaneous with the animals now lost from the surface of the globe. Our conclusion was principally based on the equal alteration of the bones, and on the manner of their deposit in the caves. We have not hesitated, therefore, notwithstanding the repugnance which our observations may occasion, to proclaim our belief, that man exists in a fossil state.”
*Annates de Chitnle, February 1833. Rose R. 2017 The Noah Code p. 271 Quoting H.H. Howorth The Mammoth and the Flood
Quoting M. Tournal’s works of 1833, Professor Fairholme tells us in 1840, p. 41: “[The] French geologists were so powerfully struck with the mixture of human and other bones, in some of the caves in the south of France, that a more strict scrutiny was instituted; and the results were published in a paper by M. Tournal, jun., of Narbonne, in No. 52 of Annates de Chimte et de Physique, from which the following is a short extract: In speaking of human remains, M. Tournal says, “The heads of the geological world would have it that they were, in all cases, recent, and accidental; and their opinions had the effect of deciding the point as a subject unworthy of further discussion. However, the discovery of the caves of Aude, of Herault, and of Gard, in the south of France, offers to the observer a crowd of human bones, and of ancient pottery, mixed up in the very same mud with those of hyenas, tigers, lions, stags, and a number of other animals of lost kinds. Attention was, therefore, again called to the subject, and MM. Marcel de Serres, Jules de Christol, and myself, after an attentive and conscientious examination, have come to the conclusion, that all these objects are of the same date, and, con- subsequently, that man was contemporaneous with the animals now lost from the surface of the globe. Our conclusion was principally based on the equal alteration of the bones, and on the manner of their deposit in the caves. We have not hesitated, therefore, notwithstanding the repugnance which our observations may occasion, to proclaim our belief, that man exists in a fossil state.”
*Annates de Chitnle, February 1833. Rose R. 2017 The Noah Code p. 271 Quoting H.H. Howorth The Mammoth and the Flood
 We must incorporate all the evidence in our thinking about Origins
We must incorporate all the evidence in our thinking about Origins
Other unexplained artifacts include deeply covered human remains, (huddled together or in scattered parts), metal, wood and objects obviously engraved or formed by mans touch. Also documented are tools, deeply buried walls, dolls, steel balls, extrusions, writing and idols. Other finds include a ceramic ladle in coal[iii] and other metal or stone utensils found in deep layers called a mystery or left undocumented by the science community. Many of these individual items were rushed to major universities for examination, who promptly characterized them as unrelated oddities and quickly dismissed their authenticity with the wave of a hand. The reference geologic strata of these sites often range in order of several to hundreds of millions of years in age, this in the scheme of “modern” geology. 2017, The Noah Code p. 80
This system referred to as the "Geologic Column" uses a scale based on the supposed evolution of animals found in each layer. Relics such as these mentioned would controvert this model and upturn the basis of a thousand mistaken books and as many PhD’s, each conferred on the basis of evolution. Yes, dogma dies hard, but sometimes it’s better to cut your losses and dispatch the dog if you wish to remain credible.
http://www.cai.org/bible-studies/fossil-artefacts-found-coal
This system referred to as the "Geologic Column" uses a scale based on the supposed evolution of animals found in each layer. Relics such as these mentioned would controvert this model and upturn the basis of a thousand mistaken books and as many PhD’s, each conferred on the basis of evolution. Yes, dogma dies hard, but sometimes it’s better to cut your losses and dispatch the dog if you wish to remain credible.
http://www.cai.org/bible-studies/fossil-artefacts-found-coal
At this juncture, we will end our tour of the human graveyards, hopefully providing the reader ample evidence with this small treatise. These finds conclusively demonstrate that the destruction of life in the course of the flood was general, and in fact was inclusive of humans as reported so thoroughly by many past authorities.
At War with the animals or the abject failure of modern paleontology?
It’s generally true that of the early North American human artifacts, many are associated with mega-fauna, weapons and arrow points. A perplexing thought is this: when we recall the decrees given by God in early Genesis, speaking only of a vegetarian based food sustenance; “For to you this shall be your food” (Genesis 1:28) and the acknowledged use of agriculture in those times, one must wonder what happened. Why is man found everywhere with a spear in hand? The intent of the First Earth was to be a bloodless co-habitation of man and animals. However, what is generally determined from these relics both in Europe and America seems to be nothing less than man was at war with the animals.
As earlier mentioned, the Bible teaches that as part of judgment man will be driven to live in caves. Perhaps an earlier rebellion forced man to live in nomadic existence and constant warfare. The Bible provides few de- tails of life in the years leading up to the Flood, only that the people had di- gressed morally to a point where they thought “only of evil continually” (Genesis 6:5). Among the flood traditions in Appendix II, we learn more details concerning this period, when law and order in society apparently vanished from the earth. The point to be made is this: the remains we examine exist in the present and cannot tell their full tale. If we remember, the earth was first shaken by the opening of the great deep, and we may assume this means earthquakes struck the planet, possibly in magnitudes and frequencies never before experienced. Assuming this being the case, with rain falling in typhoon proportions and all available shelter destroyed, where else would the survivors go? It would be reasonable to assume most would flee to the caves as their last option to escape, both man and animal. The sad conclusion is that the people and these fearsome beasts would likely perish together in savage struggles, as so often indicated in the caves. The evidence for such constantly prevails in the excavations covered in this volume, suggesting the observed evidence actually represents a short period frozen in time, a mere snap-shot of the life and death struggle for survival within the first weeks of the Flood year. If this be the case, modern archeology and paleontology would be entirely in error relative to stories about early life, lacking this perspective. So it would appear early man lived in such a state constantly; but the in actual fact, this was not the case at all. Fires in caves would be an obvious response, all souls being soaked and cold due to the rain and resultant lower temperatures.
The words of Jesus seem to resound in what is found buried across this planet, both of animal and Man, so quoted from the Bible here:
"And knew not until the flood came, and took them all away; so shall also the coming of the Son of man be.”
Matthew 24:39
At War with the animals or the abject failure of modern paleontology?
It’s generally true that of the early North American human artifacts, many are associated with mega-fauna, weapons and arrow points. A perplexing thought is this: when we recall the decrees given by God in early Genesis, speaking only of a vegetarian based food sustenance; “For to you this shall be your food” (Genesis 1:28) and the acknowledged use of agriculture in those times, one must wonder what happened. Why is man found everywhere with a spear in hand? The intent of the First Earth was to be a bloodless co-habitation of man and animals. However, what is generally determined from these relics both in Europe and America seems to be nothing less than man was at war with the animals.
As earlier mentioned, the Bible teaches that as part of judgment man will be driven to live in caves. Perhaps an earlier rebellion forced man to live in nomadic existence and constant warfare. The Bible provides few de- tails of life in the years leading up to the Flood, only that the people had di- gressed morally to a point where they thought “only of evil continually” (Genesis 6:5). Among the flood traditions in Appendix II, we learn more details concerning this period, when law and order in society apparently vanished from the earth. The point to be made is this: the remains we examine exist in the present and cannot tell their full tale. If we remember, the earth was first shaken by the opening of the great deep, and we may assume this means earthquakes struck the planet, possibly in magnitudes and frequencies never before experienced. Assuming this being the case, with rain falling in typhoon proportions and all available shelter destroyed, where else would the survivors go? It would be reasonable to assume most would flee to the caves as their last option to escape, both man and animal. The sad conclusion is that the people and these fearsome beasts would likely perish together in savage struggles, as so often indicated in the caves. The evidence for such constantly prevails in the excavations covered in this volume, suggesting the observed evidence actually represents a short period frozen in time, a mere snap-shot of the life and death struggle for survival within the first weeks of the Flood year. If this be the case, modern archeology and paleontology would be entirely in error relative to stories about early life, lacking this perspective. So it would appear early man lived in such a state constantly; but the in actual fact, this was not the case at all. Fires in caves would be an obvious response, all souls being soaked and cold due to the rain and resultant lower temperatures.
The words of Jesus seem to resound in what is found buried across this planet, both of animal and Man, so quoted from the Bible here:
"And knew not until the flood came, and took them all away; so shall also the coming of the Son of man be.”
Matthew 24:39

